Medical
Quality Made Us Global
For Everyone’s Health: Medical Molding Plastics at Global Plastics
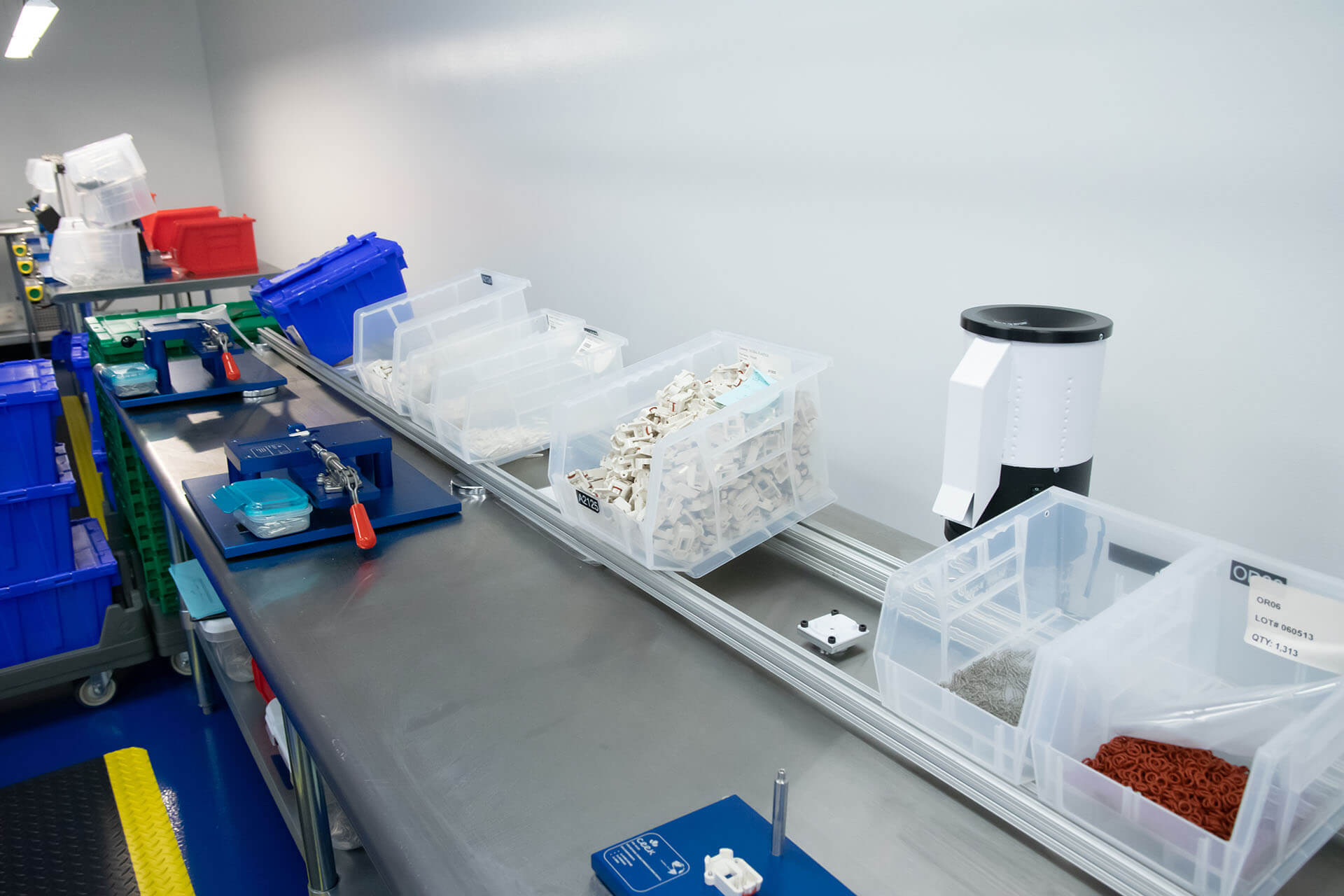

Thermoplastic Injection Molding for Medical Devices and Components
The process that results in finished, high-quality plastic medical devices and related components requires a number of key pieces to be in place. In the product design phase, the device or part must be conceptualized with design engineers to determine essential specifications and parameters, including intended use. Early on in this process, choosing the right plastic material for the project is critical—and there are thousands from which to choose.
The prototyping phase allows for short runs using a prototype mold (often tooled in aluminum) in order to ensure the product specifications are optimal before investing in the tooling of a steel production mold. Along the way we will have also determined which of our fleet of 70+ injection molding machines are best suited for full production runs of the plastic item. As a manufacturing process, custom injection molding is often the most cost-effective solution for many medical devices and parts.
Plastic Injection Molding Medical Device Applications
While the number of different plastic devices and components used in the medical industry and dental industry seem nearly infinite, there are a variety of “usual suspects” in constant high demand among injection molding manufacturers, including the following:

- Test Strips: Millions and millions of chemical test strips are used every year with diagnostic meters to check people’s cholesterol levels, including HDL, LDL, and triglycerides.
- Catheters: These thin plastic tubes are used for a huge range of medical applications. Depending on the medical-grade materials used and how the catheters are manufactured, they can be used in cardiovascular, urological, gastrointestinal, neurovascular, and ophthalmic applications. These can include fluid drainage, fluid and drug delivery, surgical instrument access, and many other medical tasks.
- Biopsy Needles: Millions of biopsies are done every year, most of which involve the use of biopsy needles attached to a plastic handle that was injection molded.
- Check Valves: Among the most common fluid delivery components, check valves are also used in fluid drainage and irrigation applications. Medical grade check valves control flow rates of fluids.
- Orthopedics: Injection molding can be used to manufacture any number of orthopedic implants, prosthetic devices, components, and related surgical instrumentation.
- Urology Pumps: Injection molded plastic urology pumps are used in treating incontinence and erectile dysfunction, as well as some surgical procedures such as endoscopy.
Applicable regulatory frameworks must be consulted, whether those of the FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) or ISO 13485 standards related to medical devices, and whether clean room or white room manufacturing environments are needed.
Plastic Materials for Medical Injection Molding
The number of different plastic resins available today is staggering. Choosing the right plastic material is an essential step for any plastic medical device or component based on its intended application. Available plastic materials include the following:
- Acrylic: Excellent transparency when needed, good tensile strength, and consistent shrinkage values make exact dimensions easy to achieve. It can also be combined with a variety of other thermoplastic materials in copolymer formulations for specific characteristics.
- ABS: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene is good for applications that require a relatively inexpensive plastic that can withstand external impacts due to its strength and stiffness. Its formulation can be modified to enhance certain characteristics as required.
- PBI: Polybenzimidazole is among the highest performance engineered thermoplastics with high heat resistance.
- PE: Polyethylene is available in both low-density (LDPE) and high-density (HDPE) formulations, with LDPE being on the softer side and HDPE being on the stiffer/harder side.
- Homopolymer Thermoplastics: This is a whole category of thermoplastic materials composed of a single monomer. Wide-ranging characteristics are available from such materials as PP (polypropylene), PC (polycarbonate), PE (see above), PBT (polybutylene terephthalate), and so on.
- Copolymer Thermoplastics: Another broad category of thermoplastic materials made by combining two or more monomers, such as ABS (see above), PVC (polyvinyl chloride), SAN (see below), PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene or Teflon), and many others.
- PET: Polyesters are good for a wide range of applications thanks to their strength, stiffness, toughness, chemical resistance, and dielectric properties. PET is the most common of all polymers, and additional options in polyesters include PBT (polybutylene terephthalate) and PETG (polyethylene terephthalate glycol.
- TPU: Thermoplastic polyurethane exhibits excellent elasticity, transparency, and resistance to abrasion, grease, and oil.
- SAN: Styrene acrylonitrile is often used to replace polystyrene when greater thermal resistance is needed. It has good toughness, rigidity, and dimensional stability and offers excellent chemical resistance. SAN medical devices can be put in an autoclave for sterilization.
- PEEK: Polyether ether ketone is excellent for medical devices because of how it tolerates gamma radiation exposure and can withstand sterilization in an autoclave.
- PSU: Polyphenylsulfone is often used in a wide range of fluid handling applications, and especially when those fluids might be hot as it retains its strength even at high temperatures.
The above is just an overview of a small sample of plastic resins available for use in the injection molding process for medical and dental devices. Rest assured the experts at Global Plastics will know which plastic material is the best option for your specific project.
Global Plastics: Precision Medical Device Injection Molding Services
With decades of experience in managing a diverse range of injection molding projects from beginning to end, Global Plastics invites you to learn more about our services. We work tirelessly to achieve cost effectiveness while maintaining the highest quality possible for every medical device, part, or component we produce. Our ability to efficiently deliver a solution that achieves the desired result is how we’ve built our reputation in this highly competitive industry with each customer client. We’d be honored to do it for your company as well. Use the contact us form on our website to learn more about our plastic medical device injection molding services.
Global Plastics has Safe Quality Food (SQF) certification for manufacturing food packaging materials and plastic molded food closures.