Quality Made Us Global
Secondary Operations
Hot Plate Welding at Global Plastics
When two different thermoplastic parts need to be joined into one, there are a variety of ways to get the job done. Among the value added assembly services we offer at Global Plastics is hot plate welding technology. Precise process controls using the right materials and equipment can result in a molecular bond in which the strength of the welded joint equals or exceeds the strength of the rest of the part.
Parameters and Process for Hot Plate Welding
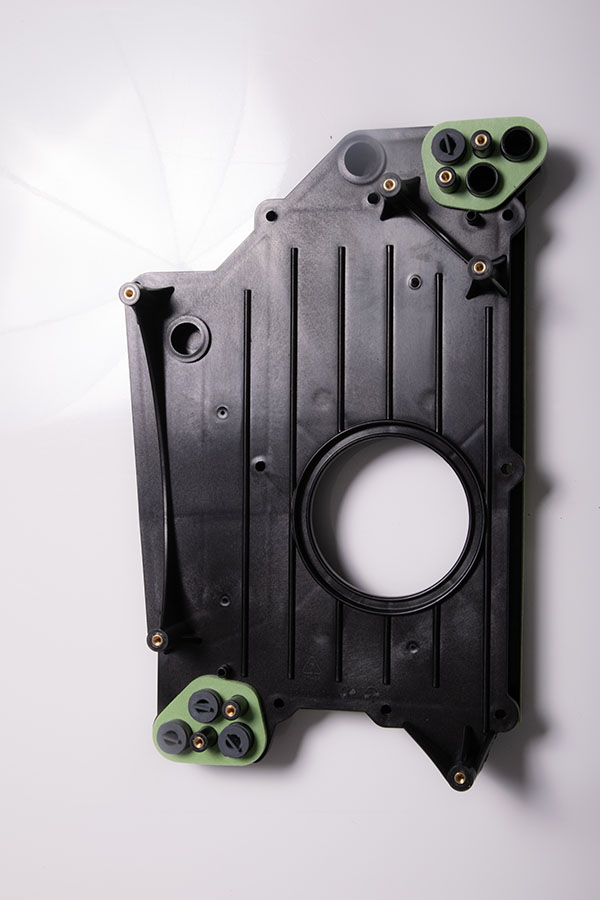


Temperature, pressure, and time are the key parameters during the hot plate welding process. The right temperature of the heated plate is typically 86° to 212° F above the melting temperature of the material being welded. Pressure of the parts against either side of the hot plate typically ranges between 0.2 and 0.5 MPa so the parts will conform to the plate, which has the desired geometric shape of the weld. When weld surfaces of the parts to be joined have been conductively heated and melted sufficiently, the plate is removed and the molten plastic of the two parts are then pressed together to form a molecular bond and often hermetic seal. The pressure is applied long enough for the part to cool to below its melting point so it can be safely removed from the machine and allowed to further cool to room temperature.
If the parts must make physical contact with the hot plate for the purposes of conforming to a specific geometric shape of the weld, the plate will be coated with Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) to prevent melted material from sticking to the hot plate, which could comprise the quality of subsequent welds. In other cases, the two plastic parts don’t need to make physical contact with the hot plate and are instead held in close enough proximity to the plate to achieve the desired level of melting through convection and radiation heating. This variation requires the hot plate to reach much higher temperatures ranging from 572° to 752° F above the material’s melting point.
Precise Control of the Hot Plate Welding Process
The bond achieved with hot plate welding is very strong. The more precise the control of the parameters involved, the higher the quality of the weld. Pressure during the heating phase of the process must be sufficient to ensure full contact with the hot plate but without causing the parts to deform. The temperature of the plate must be high enough and time of the heating phase long enough to achieve a sufficient depth of melt. If the melt depth is too thin, the result is a brittle weld. If the melt depth is too thick, there will be excess flash and unfavorable orientation of molecules at the joint interface.
During the welding phase when the molten plastic of the two parts is pressed together, the pressure must be enough to form a strong molecular bond and squeeze out any air to form an air-tight bond. If the pressure is too high, too much molten plastic will squeeze out of the weld area, resulting in a weaker bond and deformed part.
Hot plate welding is a relatively simple process, and it has fewer material compatibility constraints relative to ultrasonic welding. It can be used to join any thermoplastics or thermoplastic elastomers with a melting temperature range that falls below their decomposition temperature. Below are some of the more common thermoplastic combinations that work with hot plate welding:
- ABS – PC
- ABS – SAN
- ABS – PMMA
- PMMA – PC + ABS
- PC – PC + ABS
Factors affecting weldability include additives (stabilizers, lubricants, processing aids, coloring agents, reinforcing materials) and water content. Amorphous thermoplastics that absorb water from the surrounding air could have enough water content to cause bubbles to form during heating and joining phases that reduces the strength of the weld.
Hot plate welding has proven to be a go-to method of plastic welding in automotive industry applications. For example, ABS tail light housings can be hot plate welded to PMMA or PC lenses utilizing a modified butt joint. While the melting points of ABS and PMMA are close enough to be accomplished with a single hot plate, PC’s melting point is higher than ABS that dual hot plates are required for. Cycle times of 60 seconds can be accomplished with a high-temperature variation of hot plate welding. Other automotive components that can be assembled using hot plate welding include fuel tanks, battery cases and lids, carburetor floats, coolant and washer fluid reservoirs, and ventilation ducts.
Because plastic pipes have become increasingly common, hot plate welding is used to join plastic pipes in a variety of joint configurations, including butt, socket, and saddle/sidewall joints.
Other common applications for hot plate welding include assembly of PVC window frames, dishwasher spray arms, medical needle disposal boxes, steam iron reservoirs, PP transport pallets, and HDPE barrels.
From our headquarters in Indianapolis, Indiana, Global Plastics has been meeting the plastic injection molding, tooling, and assembly needs of clients across North America and beyond since 1992. Our expertise in plastic injection molding combined with a full-service, in-house mold tooling department, as well as value-added assembly services make us a one-stop shop for a growing number of manufacturing customer clients in need of high-quality plastic products, parts, and components. We invite you to get in touch using the contact us page of our website to begin a conversation about your needs and how we can meet them.