Quality Made Us Global
Product Development
The APQP Process at Global Plastics: Production and Quality Planning
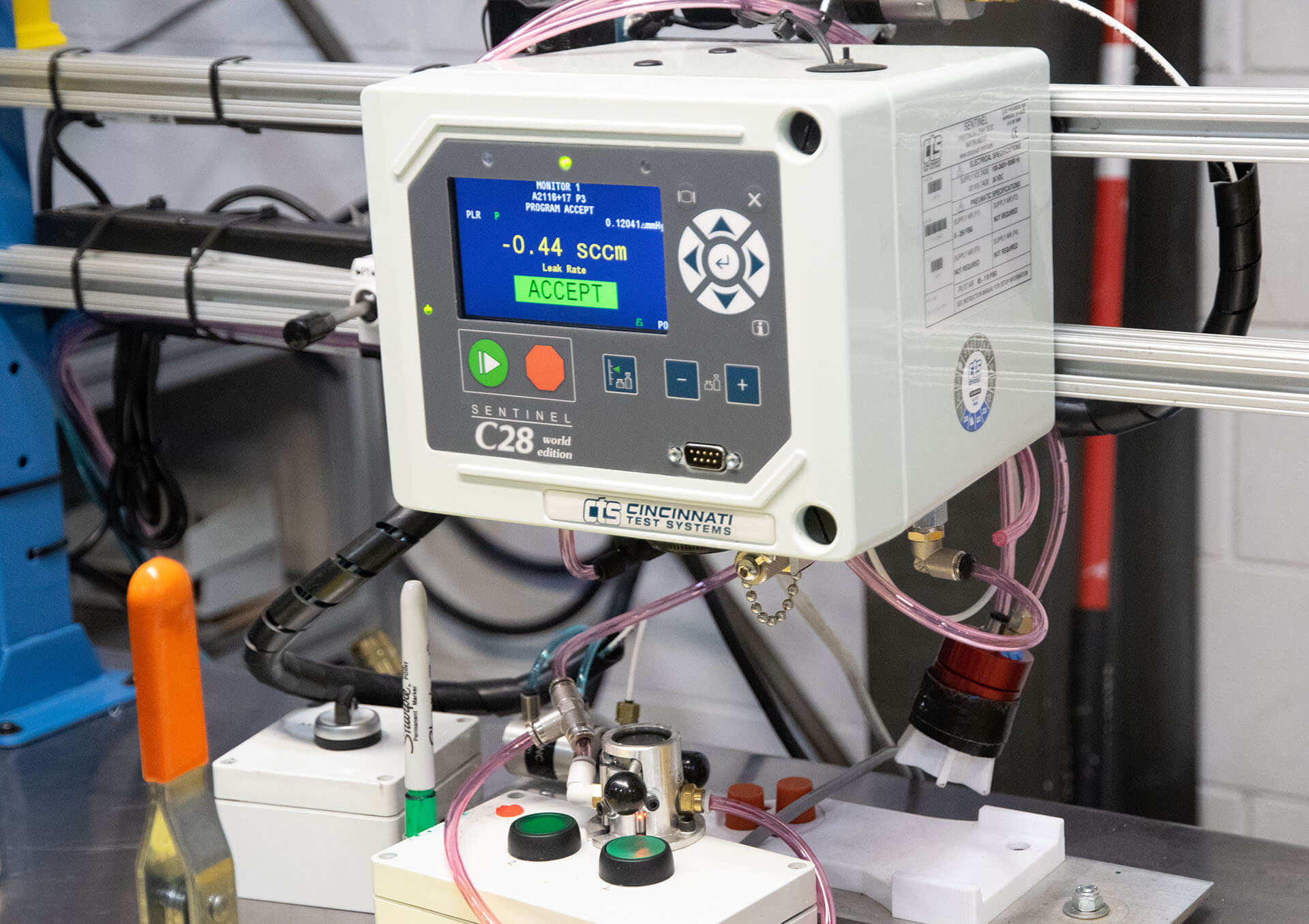

All manufacturing companies talk about the concept of “quality,” but whether it’s a meaningful commitment backed up by real practices and documenting validation is another thing entirely. At Global Plastics, our commitment to quality is a core value on full display in every customer project we take on. We utilize a structured process called APQP—advanced product quality planning—and we apply it on every product or part we handle. This is how we achieve high customer satisfaction with our clients. Learn more about the APQP process as we use it at Global Plastics.
Quality control and quality assurance are often used interchangeably, but there are subtle differences. Quality control focuses on defect detection and rejection, whereas quality assurance is about prevention of defects and mistakes in manufactured products by introducing quality concerns and practices earlier in the process. For manufacturers, quality management practices are enshrined in the ISO 9000 family of quality standards, including 9001, 9002, and 9003. Manufacturing that keeps quality in the spotlight requires careful, detailed planning for every stage of the process from product development to design to production. A comprehensive quality plan with full document validation provides guidance to the manufacturer when developing, designing, and then producing any given product, part, or component with the ultimate goal of achieving customer satisfaction.
Advanced product quality was first shaped in the automotive industry during the 1980s. Experts representing each of the big three automotive original equipment manufacturers spent five years developing APQP, which has been adopted across a range of other manufacturing sectors. When adopted and implemented, APQP helps minimize the risk of failure in the production process. What is required in the APQP process? There are seven major elements and five phases outlined below:

1. Understanding the needs of the customer: A foundational principle in APQP is reaching a full understanding of what a customer wants, needs, and expects in a product. This is required in order to plan accordingly to meet customer needs.
2. Proactive feedback and corrective action: In the APQP process, feedback isn’t just an afterthought. Instead, it is a core focus that drives corrective action to achieve better results.
3. Designing within the process capabilities: This is where the notion of design for manufacturing and assembly (DFMA) comes into play. At Global plastics, we plan and execute each project within the parameters of our known existing capabilities for no surprises.
4. Analyzing and mitigating failure modes: A key tool used in multiple phases of the APQP process is FMEA— failure mode and effect analysis.
5. Verification and validation: Verification and validation is built into APQP throughout the process. Designing products and processes is one thing, but unless they are also validated and verified through testing, the risk of failure increases dramatically.
6. Design reviews: Thorough review of designs is essential.
7. Control special/critical characteristics: Defining the critical characteristics having a significant impact on the product’s viability and use, such as safety, performance, form, fit, producibility, service life, and so on to ensure planning takes them fully into account.
1. Plan and define program: In this phase, the idea is to start planning by thoroughly exploring and understanding the customer’s needs and expectations for the product. This typically involves determining product characteristics, and then developing the quality program that spells out the design, reliability, and quality goals.
2. Product design and development verification: Designing the product is the goal in this phase, including review and verification of overall design, material specifications, equipment requirements, control plans for product prototyping, and a design failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA) for assessing failure probabilities.
3. Process design and development verification: This phase is about designing the actual process that will be used to manufacture the product or part in the quantities needed by the customer with an emphasis on efficiency. Components here include a process flow configuration, another FMEA to identify and address risks, operationalizing process quality specifications, and determining any finishing and packaging details.
4. Product and process validation and production feedback: Thorough testing is engaged for validation and verification purposes. Components include confirming capability and reliability of manufacturing process, quality acceptance criteria, trial production runs, product testing to confirm effectiveness of production process, making any and all needed adjustments before proceeding.
5. Launch, assessment, and corrective action: Full production mode is entered, but it is combined with ongoing evaluations for continuous improvement purposes. This includes collecting and analyzing customer feedback data related not only to the product or part, but also for improving customer service.
A significant output of the APQP process is the production part approval process (PPAP) with its own set of key elements and required documentation assembled throughout APQP. Other key tools used in APQP include Measurement systems analysis (MSA) and statistical process control (SPC).
Any American manufacturing company that is truly walking its talk when it comes to quality ought to know the APQP process and its related tools inside and out. This expertise should include all the applicable industry standards found in ISO 9000, along with APQP and DFMA. At Global Plastics, we are deeply familiar with all these tools and standards because quality has been central to everything we do since day one. The APQP process is rigorous, and we put each and every product or part we handle through it to ensure ultimate customer satisfaction. These quality management systems and protocols are how we steer each project through the entire development and production cycle.
If it’s time for your company to work with a plastic injection molding partner who knows how to plan for quality throughout product development, design, prototyping, and production, get in touch with Global Plastics through the contact us page of our website and we’ll be happy to learn more about your needs.
Prototyping and testing is faster and more cost-effective when done by the full-service partner who will also handle production runs.